29 Dec Cloud connect | Connectivity solutions for accessing cloud services
An overwhelming number of businesses from all industries are adopting cloud computing (or the cloud) for many applications, creating a huge demand for cloud connectivity solutions. While broadband Internet is adequate for connecting users to personal cloud applications, cloud connect solutions for connecting businesses to mission critical processes, applications, and data must be efficient and secure. Ethernet dedicated Internet and carrier Ethernet services are taking center stage in connecting businesses, governments and other institutions to the cloud.
A note on the cloud and the three cloud service models – SaaS, PaaS and IaaS
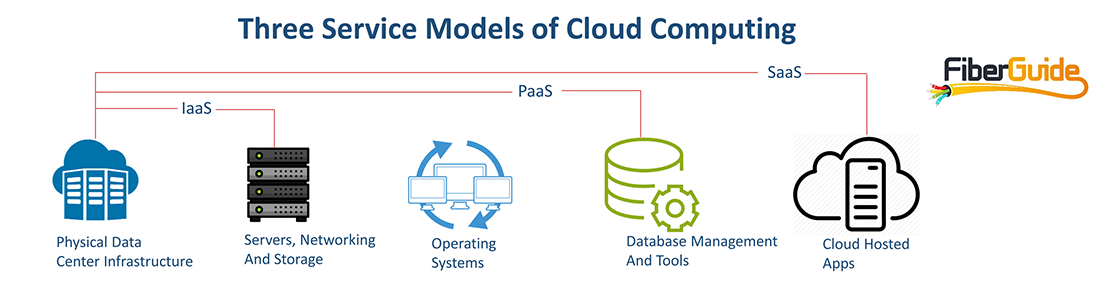
Cloud computing is the access of digital services, including infrastructure, computing platforms or software over communication networks. The cloud is gaining prominence because of its convenience and the significantly lower cost of accessing readily available IT services without the need to invest huge sums of money in data center infrastructure, computing hardware, software or expertise. With cloud computing, even the smallest of businesses can now afford to access services that were previously reserved for the largest of enterprises.
There are three main models of cloud services, namely Software as a Service (SaaS), Computing Platform as a Service or Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
SaaS is the most commonly accessed cloud service. By having instant access to software online, one bypasses the need to purchase the software and installing it locally. SaaS can range in complexity from webmail to software used for tracking expenses for a large number of employees. Some examples of SaaS include:
- Microsoft Office 365
- Google Docs
- Tableu
- Hubspot Contacts
- CISCO Webex
- SAP Concur
- Adobe Docusign
- Citrix GoToMeeting
PaaS is an application development and deployment environment on the cloud. It can be used for the development of simple applications to sophisticated large enterprise applications. All the required resources such as operation systems, database management and data storage are readily available to the user online. Popular examples of PaaS include:
- Amazon Elastic Beanstalk
- Google App Engine
- Heroku
- com
- Microsoft Azure Webb Apps
- IBM Bluemix
- Salesforce
IaaS is readily available IT i犀利士
nfrastructure (physical or virtual). While the user has to purchase, install and configure their own software, they avoid the huge costs required for buying and managing servers and complex data center environments. Examples of IaaS include:
- Amazon Elastic Computing (EC2)
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines
- DigitalOcean
- HP Converged Infrastructure
- Google Compute Engine
- IBM Cloud Virtual Servers
- Century Link Cloud Application Manager
- Peak 10
Cloud services can also be categorized as public or private. In a public cloud, users share the same hardware, storage and other network devices with other individuals or organizations. Some hosting services, webmail services and other widely used cloud services are on the public cloud.
In a private cloud, computing resources are restricted to one organization. The infrastructure and associated computing services are maintained on a private network. Organizations such as government departments and financial institutions opt for the private cloud model to guarantee security and to have the flexibility to configure resources to meet their unique requirements.
Cloud Connect– The Ethernet Advantage
Most cloud services are accessed over the public Internet because Internet access is cheap, convenient and available everywhere. However, the cheaper the access to the cloud, the less suitable it is for mission critical applications. Depending on the cloud service to be accessed, different connectivity options are available – mass market or “best effort” broadband Internet, dedicated Internet access and private networks.
Mass market broadband is ubiquitous and is available to over 3 Billion people worldwide (or 55%) of the global population. This is the most suitable solution for connecting masses of people to the cloud. Social media services, public webmail services, personal online image storage and management, and many other personal online services are accessed using mass market broadband Internet. This form of Internet connection is usually shared so that download speed fluctuates depending on the number of users sharing the service at any given time. While broadband Internet access is adequate for most cloud applications, if security is a concern the user should consider an encryption solution, such as a VPN Service.
For public Internet access to cloud services requiring consistent bandwidth that does not fluctuate, dedicated Internet access is a must. Dedicated Internet access is a connection between the user’s premises and the Internet service provider (ISP) exclusively for one subscriber. Dedicated Internet access comes with a service level agreement (SLA) which guarantees bandwidth, uptime and may also include latency, packet loss and jitter.
Uptime is a measure of the time the connection is operational and typically range from 99.5% to 99.999% (the so called 5 nines). While the difference might look trivial, these uptimes translate to 1 day of downtime per year for 99.5% and 5 minutes of downtime per year for the 99.999% uptime.
Examples of cloud services requiring reliable dedicated Internet include video conferencing, access to health information systems and online training.
Ethernet dedicated Internet
Ethernet is becoming the de facto dedicated Internet access technology of choice and has overtaken legacy technologies such as T1/E1 lines and SONET/SDH. Flexibility, high bandwidth and low cost per bit are some of the attractive attributes of Ethernet.
Ethernet dedicated Internet access is flexible in that a user can sign up for low bandwidth and be able to upgrade as soon as more bandwidth is required. A subscriber can sign up for as little as 1 Mbps and upgrade it in steps of 1 Mbps. In comparison, a T-1 line will deliver 1.5 Mbps with an incremental option of 1.5 Mbps using bonded copper pairs.
With the Institute for Electronic and Electrical Engineers work group, IEEE 802.3z, relentless work on higher speed transmission, Ethernet is now capable of delivering up to 400 Gbps. Typical Ethernet dedicated Internet speeds of up to 10 Gbps are readily available from a large number of providers. This is adequate for most cloud applications accessed over the public Internet.
The low cost per bit is a very attractive attribute of Ethernet dedicated Internet, especially for subscribers requiring higher data rates. A $10,000/month 10 Gbps Ethernet dedicated Internet subscription (using Ethernet over Fiber) translates to $1/ Mbps. Please note that actual prices depend on the provider, location, SLA, contract terms and other factors. Refer to GeoQuote for Ethernet dedicated Internet pricing in your area.
Ethernet over Fiber is available in lit buildings but only about 1 in 4 buildings are connected to one or more network providers. Ethernet over Copper is more readily available and is more cost effective. However, speed is typically limited to a maximum 50 Mbps. Check Geoquote for availability in your area.
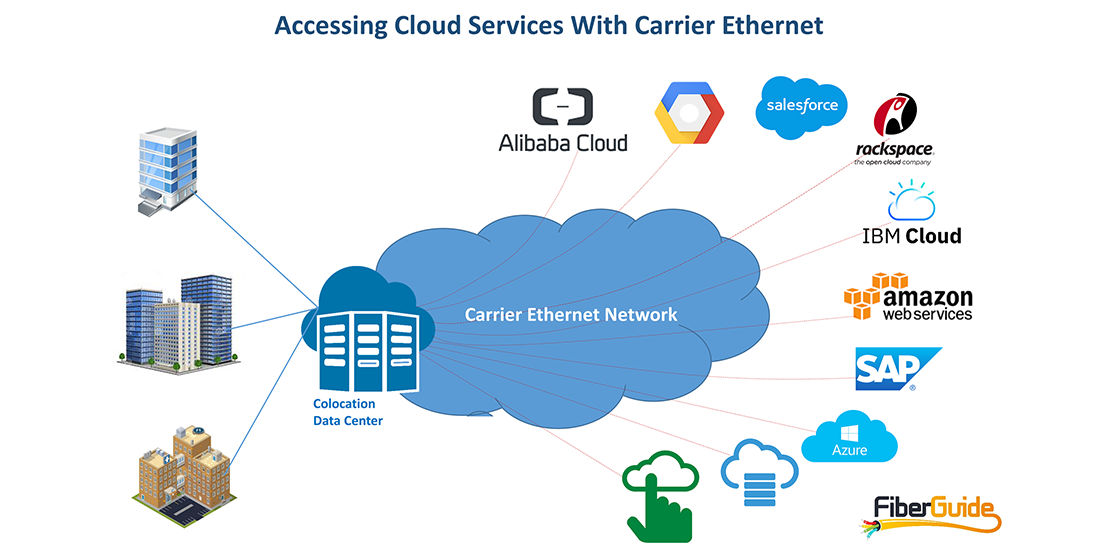
Cloud Access Using Private Carrier Ethernet Services
Organizations such as governments, financial institutions and others with sensitive applications are apprehensive about using the public Internet for cloud access. Instead, they opt for private networks such as MPLS, carrier Ethernet and optical wavelength services.
Carrier Ethernet services are gaining momentum as a technology of choice for cloud access. Ethernet Private Lines and Virtual Private LAN Services as discussed in the blog, Options for Accessing Carrier Ethernet Services, are most commonly used for cloud access. With these services, businesses can bypass the public Internet and avoid all the negative issues associated with the Internet. In particular, the following advantages are realized:
Data center connectivity – All data centers are equipped to instantly accept Ethernet connections. This makes connections to colocation facilities quick and relatively inexpensive.
Scalability – as with all Ethernet services, carrier Ethernet is highly scalable. Users can change their bandwidth swiftly without the need for any additional equipment on premises.
Better security – in addition to other security features that come with carrier Ethernet services, the network is completely isolated from the public Internet. There is no risk of malicious attacks that have become synonymous with the public Internet.
Superior quality – carrier Ethernet comes with better QoS including better reliability, latency, packet loss, and reduced number of hops between premises and the cloud services.
Better redundancy – carrier Ethernet networks have built in resilience that mitigates against long down times.
Simplicity – since local area networks (LANs) use Ethernet, the use of carrier Ethernet allows for an all-Ethernet infrastructure, simplifying network management. The alternative option of using MPLS for cloud connect requires that all network devices and management tools are compatible with both MPLS and Ethernet.
The customer premises may be connected directly by a provider’s carrier Ethernet service to the cloud. Alternatively, connections can be accomplished through the cloud provider’s connection solution usually available in a colocation data center. One of the most popular cloud connect solutions is Amazon’s AWS direct connect which facilitates user connections to the Amazon cloud. Because it is Ethernet compliant, IEEE 802.1Q, the solution can be seamlessly connected to a customer’s carrier Ethernet service.
Summary | FiberGuide free support
There is a wide range of network permutations for connecting premises to cloud services. A suitable choice for a solution depends on a number of factors including availability (which solutions are readily available to the user?), bandwidth requirements, level of security, and cost considerations. While broadband Internet is the most readily available and is cheap, it is only suitable for personal and less critical business applications.
For more mission critical cloud applications, a dedicated Internet connection or private network solution is required. When dedicated Internet or a private network are essential, Ethernet offers the most flexible, high bandwidth and cost effective option.
Using online carrier research tools and a large network of carrier provider partners, FiberGuide assists users to sort through the wide range of possibilities. FiberGuide product specialists are available to customers as a free resource. They will match customers’ technical requirements with one or more network provider solutions.
In addition to narrowing down options and providing the best pricing, FiberGuide product specialists will also work with customers through provisioning and beyond implementation. In other words, in addition to having a direct relationship with the network provider, they will remain as an ongoing resource to help the customer with any questions or issues they may have with their selected provider.
Founder and Technical Director at FiberGuide, Lecturer, Scientist and Engineer. Passionate about optical networking and information and communication technologies. Connect with me on Linkedin – https://www.linkedin.com/in/jabulani-dhliwayo-1570b5b


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.