
04 Nov What is IP Over DWDM and What are its Challenges?
In the high-speed data transmission landscape, IP over DWDM (IPoDWDM) has become a cornerstone technology, adept at fulfilling the burgeoning need for bandwidth. This method synergizes the expansive capacity of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) with the universality of Internet Protocol (IP), enabling the direct transmission of data packets via optical networks. IPoDWDM optimizes data flow by consolidating traditionally separate network layer functions into the optical layer, enhancing efficiency, and potentially curtailing the necessity for signal conversions.
Central to this architecture are IP routers, orchestrating data packet traffic at network nodes, and DWDM systems, propelling these packets through extensive optical channels. The strategic placement of pluggable transceivers into IP routers represents a shift from conventional transponders, promising cost reductions and simplified operations. Although IPoDWDM excels in scenarios such as data center interconnects and certain metropolitan networks, it is accompanied by a set of challenges that warrant a closer examination.
Difference between IPoDWDM and Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Before delving into the complexities of IPoDWDM, it is essential to distinguish it from its foundational technology, Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM). While WDM is a method that multiplexes multiple optical carrier signals on a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths, IPoDWDM takes this a step further by integrating IP directly into the DWDM layer. This integration is designed to streamline the network infrastructure, allowing for a more efficient and direct data packet delivery without the intermediate conversion steps typically required in traditional WDM systems.
To elucidate the advancements IPoDWDM brings to the realm of optical networking, it is instructive to compare it directly with Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM), the technology upon which it is based. Check out our comparison table below:
| Feature | DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) | IPoDWDM (IP over Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A fiber-optic transmission technique that increases bandwidth by sending different data streams over various wavelengths of light. | An innovative approach that combines IP routing directly with the optical signaling of DWDM, enabling more efficient data packet transmission. |
| Layer Integration | Operates primarily at the physical layer, dealing with light transmission across the fiber. | Integrates network layer (IP) functionalities directly into the physical layer, streamlining the data transmission process. |
| Equipment Separation | Typically requires separate IP routers and DWDM systems for data processing and light transmission. | Employs pluggable transceivers within IP routers, reducing the need for separate DWDM systems and equipment. |
| Data Rates | Supports high data rates but is primarily focused on the transport layer capabilities. | Designed to handle extremely high data rates suitable for modern internet traffic demands, leveraging the DWDM infrastructure. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable in terms of bandwidth but requires additional equipment for network layer functionalities. | Enhances scalability by combining IP routing and optical transport, potentially reducing the overall footprint of network equipment. |
| Operational Complexity | Complexity is contained within the optical layer and its signal management. | Adds complexity by merging the management of IP and optical layers, requiring a more integrated approach to network operations. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-efficient in terms of pure transport capacity but may require additional investment for IP layer management. | Can offer cost savings by reducing equipment and simplifying the network architecture, though it may introduce new costs related to integration. |
| Flexibility | Offers flexibility in optical transport but is dependent on higher layers for routing and switching. | Provides a more flexible and efficient network by reducing the dependency on separate routing and switching layers. |
| Innovation Pace | Innovations are typically focused on improving capacity and efficiency within the optical layer. | Must keep pace with innovations in both IP routing and optical transport, which can be challenging given the rapid evolution of networking technologies. |
Five Challenges of IPoDWDM
Operational Complexity
The implementation of IPoDWDM introduces a significant degree of operational complexity. The fusion of IP with the optical layer necessitates precise coordination between previously independent systems. Network operators must now master both IP and optical disciplines to effectively manage the intricate routing and optical signal requirements inherent in IPoDWDM. The added responsibility of continuous network layer monitoring and optimization further compounds the operational demands, placing a heavier burden on network management teams.
Rate Evolution Issue
The rapid pace of data rate evolution presents a significant challenge for IPoDWDM technology. As consumer demand for bandwidth increases, network providers are pressured to continually upgrade their systems to support higher data rates. IPoDWDM systems, which integrate the routing and optical layers, must be designed to accommodate these evolving standards, which can be a complex and costly endeavor.
One of the primary issues is the lifecycle disparity between the IP and optical components. IP routers tend to have a shorter upgrade cycle compared to the more stable DWDM systems. This means that as new, faster IP routers are deployed, the existing DWDM infrastructure may not be fully optimized to handle the increased rates, leading to potential bottlenecks.
Furthermore, the industry is witnessing a shift towards higher-speed transceivers, such as 400ZR, which are designed for specific distances and applications. While these transceivers push the envelope on data rates, they also necessitate the redesign of existing network infrastructure to support them. This includes not only the physical hardware but also the management software that controls the network, which can be a significant operational hurdle.
The challenge is compounded by the need for backward compatibility and the ability to support a mix of different data rates within the same network. This requires sophisticated network planning and dynamic management capabilities to ensure that all components of the network can communicate effectively, without compromising performance or efficiency.
The rate evolution issue in IPoDWDM demands a strategic approach to network design and a willingness to invest in regular updates and maintenance to keep pace with the ever-increasing data rate requirements.
Oversized Pluggables
The integration of pluggable optical modules into networking equipment has been a significant trend in recent years, driven by the need for more efficient and cost-effective solutions in data center interconnects and broader network infrastructure. However, this shift has not been without its challenges. One of the primary concerns has been the physical size of these pluggables, which can be oversized for the equipment into which they are being integrated.
Despite the challenge of integrating these larger modules, the industry’s uptake has been substantial. According to a report by Cignal AI, the adoption of IP-over-DWDM and coherent pluggables is expected to impact Metro WDM spending significantly.
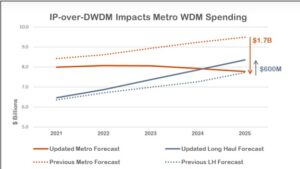
The historical growth rate of 6% is anticipated to level off as more network operators embrace these technologies. The report further highlights that the implementation of IP-over-DWDM is gaining momentum and is expected to soon only moderately affect capital expenditure. The Gen60C 400ZR/ZR+ pluggable optics are seen as a solution to the technical and operational challenges previously faced, with availability well-timed to the 400 Gigabit Ethernet investment cycle. These advancements are expected to drive early volumes, particularly in hyperscale data center interconnects, and attract service providers—who account for a substantial portion of optical CAPEX—to adopt these technologies as the cost savings become increasingly evident.
Furthermore, Cignal AI has forecasted a reduction in spending on standalone optical transport hardware by $1.1 billion in 2025, as operators introduce pluggable coherent optics into routing and switching equipment, replacing traditional and compact modular equipment. This decline is expected to be partially offset by increased sales in IP Routing and Switching hardware, open line systems, long haul WDM, and direct sales of coherent optics to hyperscale operators. This shift underscores the industry’s significant move towards pluggable modules, which, despite their size, offer more efficient, cost-effective, and flexible solutions.
The trend towards pluggables is a clear indicator of the industry’s direction, emphasizing the need for innovation in module design to address the challenge of oversized pluggables while maintaining the benefits of cost and efficiency.
Siloed Vendor-Proprietary Management and High Costs
A significant hurdle in the widespread adoption of IPoDWDM is the prevalence of siloed, vendor-proprietary management systems. These systems often require network operators to be locked into a single vendor’s ecosystem, limiting flexibility and the ability to integrate with equipment from other manufacturers. This vendor lock-in can lead to several issues:
- Limited Interoperability: With proprietary management systems, interoperability between different vendors’ equipment can be challenging. This can restrict the network operator’s ability to select best-of-breed solutions and can complicate network expansions or upgrades that involve multi-vendor environments.
- Innovation Stifling: A single-vendor focus can stifle innovation by reducing the competitive pressure to improve products and services. It can also slow down the adoption of new standards in the industry, as proprietary systems may not be quick to support them.
- Cost Implications: Proprietary systems often come with higher costs, not only in terms of initial capital expenditure but also through ongoing licensing fees, support contracts, and the cost of being tied to a single vendor for upgrades and expansions. These costs can be prohibitive for smaller network operators or those looking to scale efficiently.
- Complexity in Management: Managing a network with vendor-specific tools and interfaces adds complexity, requiring specialized training and knowledge. This can increase operational expenses and make it difficult to manage networks effectively, especially in a dynamic and evolving technological landscape.
- Negotiation Leverage: Vendor lock-in diminishes the network operator’s leverage in negotiations, potentially leading to less favorable terms and conditions. It can also limit the operator’s ability to push for customizations or specific features that are better suited to their network requirements.
To overcome these challenges, the industry is gradually moving towards open standards and interoperable systems that can work seamlessly with equipment from different vendors. However, the transition is complex and requires a concerted effort from both network operators and equipment manufacturers.
Technical Compromises and Operational Challenges
The final challenge in implementing IPoDWDM is the array of technical compromises and operational challenges that come with merging IP routing and optical transport into a single solution. These compromises can impact the performance, reliability, and manageability of the network.
- Performance Constraints: IPoDWDM requires the optical network to be tuned to support the high-speed requirements of IP traffic. This can lead to performance constraints as the optical layer is traditionally optimized for different parameters than the IP layer. Balancing these requirements often means making compromises that can affect the overall network performance.
- Reliability Issues: The integration of IP and DWDM layers can introduce new points of failure. For instance, if the pluggable transceivers in the routers fail, it can lead to significant disruptions in both the IP and optical layers. Ensuring high reliability in such an integrated environment requires robust design and redundancy that can be complex and costly to implement.
- Management Complexity: With IPoDWDM, network operators must manage both IP and optical layers simultaneously, which can be a complex task. This complexity is compounded when considering the need to maintain the quality of service, balance traffic loads, and ensure network security across both layers.
- Scalability Issues: While IPoDWDM can offer cost savings and efficiency gains, it can also introduce scalability issues. As networks grow and traffic patterns evolve, the integrated IP and DWDM systems must be able to scale without incurring exponential increases in complexity or cost.
- Technical Expertise: The convergence of IP and optical technologies requires a workforce that is proficient in both domains. However, such expertise is rare, and training existing personnel or hiring new talent can be a significant operational challenge and expense.
- Futureproofing: As network technologies continue to advance rapidly, ensuring that IPoDWDM solutions are future-proofed is a challenge. Network operators must carefully plan and invest in technologies that can adapt to future standards and requirements without necessitating complete overhauls.
The takeaway is that while IPoDWDM presents a promising approach to high-speed data transmission, it also brings a set of technical and operational challenges that must be carefully navigated. Addressing these issues requires a strategic balance between performance, reliability, and cost, as well as a commitment to ongoing training and development in the face of a constantly evolving technological landscape.
To learn more about advanced optical networking, sign up for one of our training events in optical networking.
Kihara Kimachia is a seasoned technology writer and digital marketing consultant with over 15 years of experience. His expertise spans across a broad spectrum of topics.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.